- Health risks and legal limits
- Nitrate contamination in urban areas
- Impacted States and Cities
- Nitrate contamination in water systems
- How nitrate pollution affects cities?
- How can nitrate affect babies?
Solutions to the Widespread Nitrate Problem: Safeguarding Drinking Water
Nitrate Contamination in US Drinking Water: A Growing Concern for Urban Areas In recent years, nitrate contamination in drinking water has extended beyond rural communities and small towns. It has made its presence felt in major cities and urban areas across the United States.
Nearly 60 million people in cities such as Los Angeles, Las Vegas, and other urban centers are affected by elevated nitrate levels in their drinking water. This contamination poses significant health risks, including cancer and adverse effects on infants.
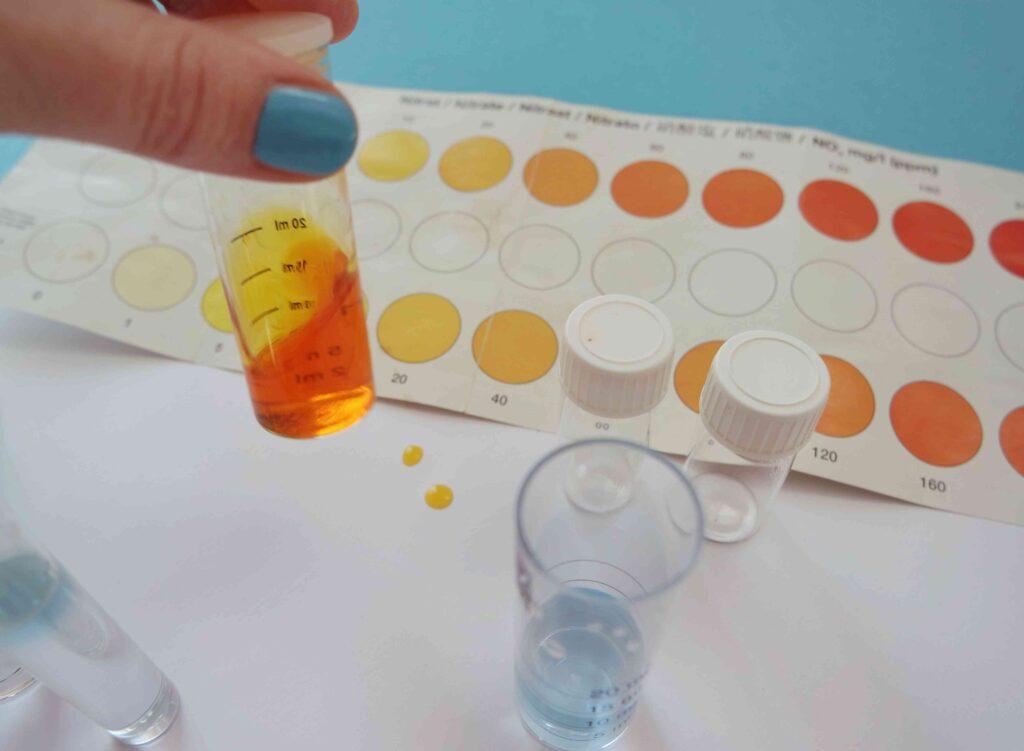

Nitrate and its sources
- Nitrate, a chemical component found in fertilizers and animal manure, can seep into surface and groundwater and drinking water sources.
- Urban runoff and municipal wastewater discharges contribute to nitrate contamination.
- Agricultural runoff remains the primary source in many states.
- Nitrate can infiltrate drinking water supplies as it flows off farm fields and enters water bodies.
The Extent of the Problem
The latest analysis by EWG examined data from 757 large or very large community water systems between 2017 and 2019. Several of these water systems had nitrate levels above 3 milligrams per liter (mg/L), considered high contamination levels. Approximately 59.5 million individuals rely on these water systems for drinking water, highlighting the widespread impact of nitrate pollution.
Health risks and legal limits
- Federal and state regulators have set a legal limit of 10 mg/L for nitrate in drinking water. This is based on recommendations from the U.S. Public Health Service in 1962 to prevent blue baby syndrome.
- But recent studies indicate that even lower levels, such as 5 mg/L, pose health risks including an increased likelihood of colorectal cancer, thyroid disease, and neural tube birth defects.
Nitrate contamination in urban areas
- Contrary to popular belief, nitrate contamination is not solely a rural issue.
- Major cities, including Los Angeles, Las Vegas, and others, where nitrate levels in drinking water exceed the legal limit.
- This unexpected presence of elevated nitrate levels in urban areas raises concerns about potential health implications for the affected population.
Impacted States and Cities in the US:
Among the states grappling with nitrate contamination, California stands out with the highest number of residents affected. Over 22.7 million state residents are supplied with nitrate-contaminated water. Besides California, Arizona, Pennsylvania, and New Jersey also have significant numbers of residents, approximately 5.2 million, 4.5 million, and 3.2 million respectively. These residents rely on nitrate-contaminated drinking water sources.
Nitrate contamination in water systems
According to the Environmental Working Group, water systems are classified as large or very large based on the people they serve.
- Out of the 757 systems examined, 410 systems affecting 37.8 million people had nitrate levels at or above 5 mg/L.
- 60 systems serving almost 3.9 million people had nitrate levels at or above the legal limit of 10 mg/L.
Nitrate contamination has been associated with agricultural areas and rural communities lately. But recent studies revealed that In some heavily populated cities, such as Los Angeles and Las Vegas, elevated nitrate levels were found.
How nitrate pollution affects cities:
Of the 757 large or very large systems with elevated nitrates, 52 percent used groundwater as their source of drinking water, and 48 percent used surface water
In order to understand how nitrate pollution affects cities, it is necessary to explore two primary types of water supply systems:
- Groundwater
- Surface water.
Groundwater Systems and Aquifer Contamination
Groundwater systems draw water from deep underground aquifers, which span vast areas. Surprisingly, pollution from agricultural activities can contaminate these aquifers, leading to nitrate presence in drinking water supplied to cities. Even if the farms responsible are far away.
Surface Water Systems and Agricultural Runoff
- Surface water systems rely on water sources like lakes, reservoirs, and rivers.
- Agricultural pollutants, including nitrates, enter surface water downstream after running off from fields upstream.
- In cities like Des Moines, Iowa, drinking water is contaminated by farm chemicals from far-off farms.
- Systems with higher nitrate levels were slightly more likely to have groundwater as their source.
How can nitrate affect babies?
Ingesting high levels of nitrate reduces red blood cells’ oxygen-carrying ability. Red blood cells usually return to normal in adults and children, but not in babies. Babies who drink formula mixed with water containing high levels of nitrate (or eat foods made with nitrate-contaminated water) may develop a serious health condition due to the resulting lack of oxygen. This condition is called methemoglobinemia, often called “blue baby syndrome.” Diarrhea can worsen blue baby syndrome. Nitrate levels in water below 10 mg/L will not affect your baby.
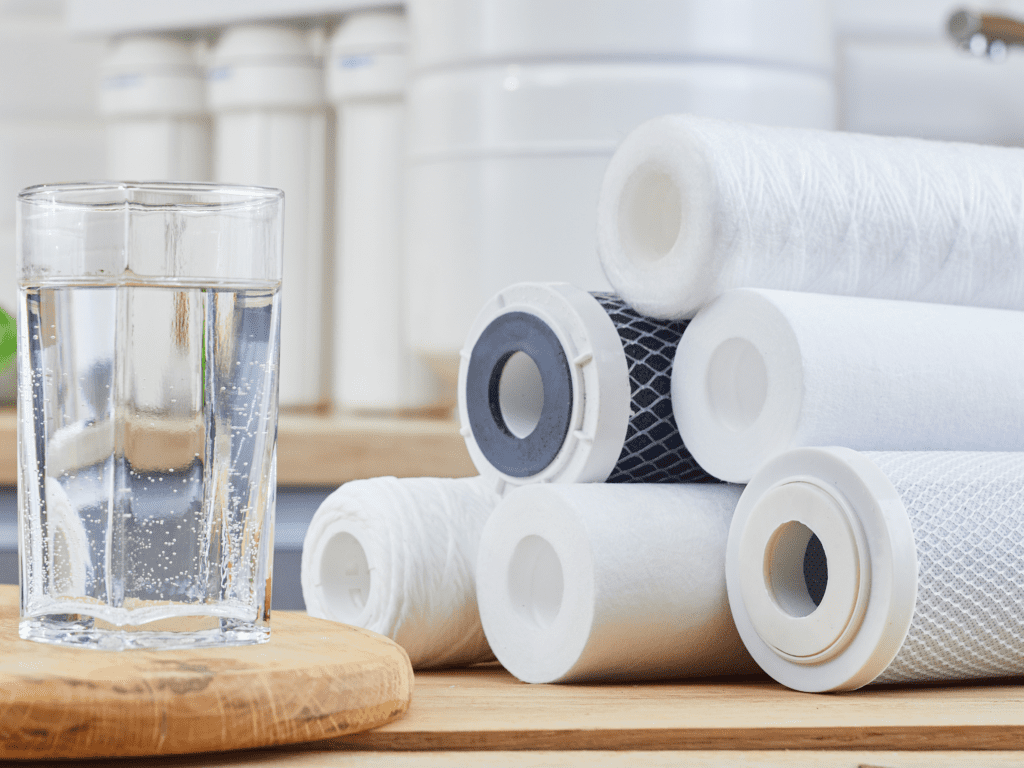

Solutions to the Widespread Nitrate Problem: Safeguarding Drinking Water
At Life Water Report, we recognize the critical importance of addressing the major issue of nitrate pollution to safeguard drinking water across the United States. As experts in the field, we understand that prevention is not only cost-effective but also paramount to ensuring community health and well-being.
To reduce nitrate contamination in your local water supply:
- Properly Dispose of Household Chemicals: Ensure that you dispose of household chemicals, such as cleaning products and pesticides, responsibly. Avoid pouring them down drains or toilets, as they can cause water pollution.
- Limit Fertilizer Use: If you have a garden or lawn, use fertilizers sparingly and follow the instructions carefully. Overapplication of fertilizers can lead to excess nitrates seeping into groundwater. Consider organic or slow-release fertilizers.
- Dispose of Animal Waste Properly: If you have pets or livestock, ensure that their waste is disposed of properly. Animal waste contains high levels of nitrogen, which can contribute to nitrate contamination if not managed correctly. Dispose of it in designated areas or consider composting it for use as a natural fertilizer.
- Install a High-Quality Water treatment system:
Nitrate removal through water treatment systems is viable. This includes water filtration systems.
- Reverse osmosis (RO) with the capability to generate alkaline water: Reverse osmosis is a proven method of removing nitrate contaminants from drinking water. This process involves passing water through a semi-permeable membrane that filters out impurities, including nitrates.
- Ion exchange: Ion exchange is another effective nitrate removal method. It involves exchanging nitrogen ions with harmless ions, such as chloride or sulfate, through a resin bed. This process significantly reduces nitrate concentrations in water.
- Biological denitrification: Biological denitrification is a natural process that utilizes microorganisms to convert nitrates into harmless nitrogen gas. This method is commonly employed in larger-scale water treatment facilities. By creating an oxygen-depleted environment, microorganisms convert nitrates into nitrogen gas, which is released harmlessly into the atmosphere.
- Activated carbon filter: Activated carbon filters are widely used for water treatment, including nitrate removal. These filters work by adsorbing nitrates onto their porous surface, trapping and removing them from the water.

To ensure thorough nitrate removal, combine multiple treatment methods into a comprehensive water treatment system.
Note: As for practical filtration and purification, we suggest you install a reverse osmosis (RO) system with a post-alkaline mineral system or install a multi-filter countertop unit that removes the majority of toxic chemicals and then creates alkalized mineral water with antioxidants. Otherwise, you have unhealthy water that is electron deficient and will take calcium from the body and cells and cause low bone density.
Check water contaminants by zip code in your area FREE:
www.LifeWaterReprot.com is the easy way to generate a water analysis of your water – at no cost to you. If you own a private well, we recommend testing for coliform bacteria and nitrate every year.
Our Life Water Quality Reports reveal the level of nitrate detected in the system serving your home. If your nitrate test results are 5 mg/L or higher, you may want to re-sample in six months.
Conclusion: In conclusion, nitrate contamination in US drinking water has emerged as a significant and growing concern, particularly in urban areas. High levels of nitrate pose serious health risks and demand immediate attention from policymakers, water management authorities, and individuals alike. It is our collective responsibility to protect our drinking water and ensure a healthier and safer future for all. Access to clean and safe drinking water for all should remain a top priority.
Visit http://www.
