Scientific research has revealed concerning evidence regarding fluoride’s neurotoxic effects, particularly on children’s developing brains. Studies have indicated that fluoride exposure can lead ent against water fluoridation informed consent. By treating fluoride as a medication, public water systems are obligated to provide individuals with comprehensive information regarding its risks and benefits.
This approach ensures that individuals can make autonomous health decisions, free from influence or undue influence.

Addressing Regulatory Oversight
In addition to the legal implications, the case against water fluoridation underscores the need for enhanced regulatory oversight and accountability. Despite persistent claims of safety and efficacy, fluoride additives in public water supplies have not undergone rigorous evaluation or obtained medical product licenses. Moreover, the source of fluoride, often derived from air pollution scrubbers, raises concerns about the presence of additional neurotoxins and heavy metals in treated water. Reevaluation of regulatory standards is imperative to safeguard public health and ensure drinking water system integrity.
Charting a Path Forward
By prioritizing scientific evidence and individual autonomy, we can strive to ensure public health interventions align with safety, transparency, and accountability.
As we LOOK into the critical subject of water fluoridation, it becomes essential to explore the potential risks associated with the fluoride added to the public water supply in the United States. Community water fluoridation is widely recognized as an effective strategy for preventing dental caries, recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO).

Health Effects of Fluorides
Fluoride, which is added to the water supply of over 73 percent of the U.S. population, is not naturally occurring. Rather, it is derived as a chemical byproduct of the phosphate fertilizer and aluminum production industries, presenting an inherent risk.
Fluoride affects the bones, teeth, skeletal muscles, and the nervous system. Fluoride poisoning symptoms are salivation, nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain (Chouhan and Flora, 2010).
Contamination by Arsenic
John F. Mueller Jr., a retired civil and control systems engineer, stumbled upon a disconcerting discovery during his review of a large municipal water utility’s fluorosilicic acid (FSA) purchasing contract.
His analysis revealed consistent arsenic contamination in FSA shipments over several years, with levels ranging from 25 to 50 milligrams per liter (mg/L).
This revelation raised alarming concerns about the safety of the public water supply and the potential health risks posed by arsenic.
Certified Chemicals for Water Fluoridation
Fluoride exposure sources in the United States have increased since the 1940s. By 1960, fluoridation of drinking water had spread to over 50 million people in communities throughout the United States
The National Sanitation Foundation (NSF) has certified three chemicals for water fluoridation:
- Hydrofluosilicic or Fluosilicic acid
- Sodium fluoride,
- Sodium silicafluoride.
According to the NSF, arsenic is the most common contaminant detected in these chemicals, while lead is another significant contaminant.
Tom Reeves, the National Fluoridation Engineer at the U.S. Centers for Disease Control (CDC), reports that the average drinking water contains 0.43 parts per billion (ppb) of arsenic attributed to the fluoride chemicals used.
Fluoridation levels should be between 0.7 and 1.2 mg/L.
John F. Mueller Jr., driven by his commitment to public health, safety, and welfare, could not remain silent upon uncovering fluoride in the water supply.
According to Mueller, an expert in the field, more than 99.5 percent of fluoride introduced into drinking water does not benefit teeth. Instead, it is used for various other purposes such as laundry, lawn irrigation, showers, and toilet flushing.
Considering Public Health and Water Treatment
Fluoride is the primary source of arsenic in water, according to the American Water Works Association. If the maximum contaminant level for arsenic is lowered to 5 ppb, fluoride additives contribute about 90 percent of arsenic.
It is essential to understand that the expense involved in removing naturally occurring arsenic from water supplies is considerable.
To remove arsenic from fluoridated water, you can employ various methods. Here are some commonly used techniques:
- Activated Alumina: Activated alumina is an adsorbent that removes arsenic from water. The water is passed through a bed of activated alumina, which adsorbs the arsenic contaminants.
- Reverse Osmosis (RO): Reverse osmosis is a process where water is forced through a semipermeable membrane, removing various contaminants including arsenic. RO systems remove arsenic and fluoride from water. RO membrane-based separation techniques offer hope for the sustainable and efficient removal of these contaminants.
- Activated Carbon Filtration: Activated carbon filters remove organic contaminants, including arsenic. However, their efficiency in removing inorganic arsenic can vary, so it’s wise to choose the right type of activated carbon filter.

The Life Sciences™ Hydrogen Alkaline Bio Energy Water System is a state-of-the-art 5-stage filtration system that ensures clean and safe drinking water by removing impurities and enhancing water quality. With features like pH enhancement, antioxidant infusion, and a Free Bonus Borosilicate Glass Pitcher with multiple uses for making coffee, tea, herb and also fruit infused alkaline beverages. Backed by a lifetime warranty, it offers a comprehensive and reliable solution for high-quality water purification “Manufacturer to You” Discount Pricing at only $297. The difference between this unit is its activated carbon filter that reduces scale buildup in pipelines. Visit link
Research your water source: Find out if your water supply has high levels of fluoride. This information is typically provided by local water authorities or obtained through water quality reports.
What is the best water filter for fluoride?
In order to keep water safe and clean, reverse osmosis has gained popularity among other filters. Due to its safety, cost-effectiveness, and ease of maintenance, reverse osmosis has become increasingly popular. For just pennies per gallon, a Family of four can drink fresh, great-tasting RO water every day
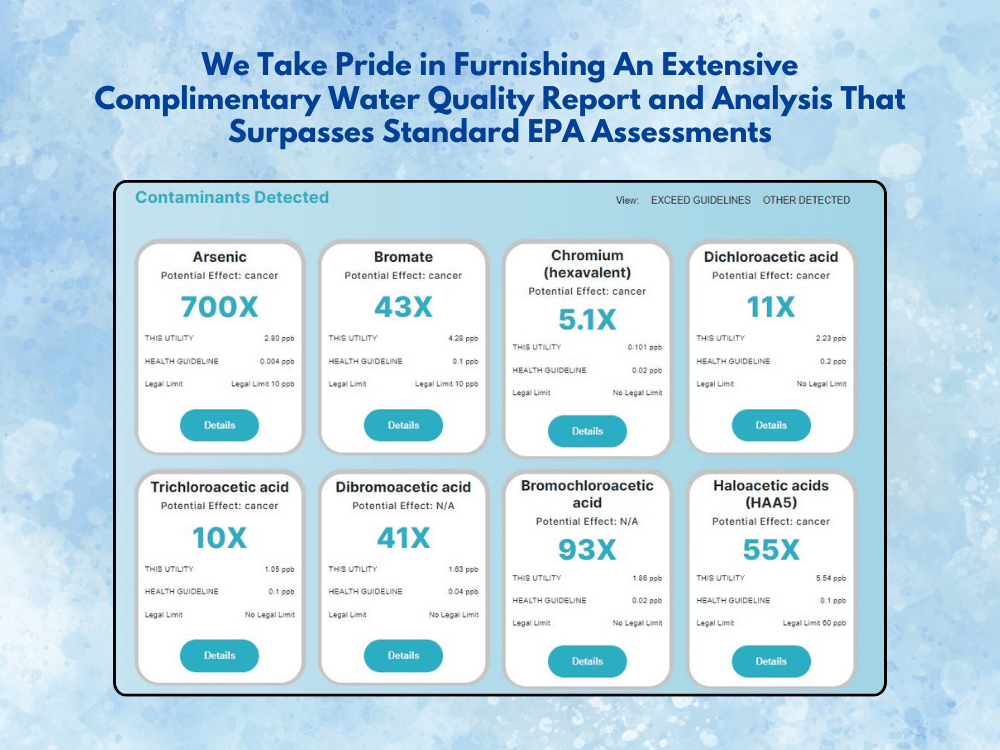
Life Water Report Offers top-quality systems at affordable prices. Our systems are manufactured with the highest quality components, come with an outstanding warranty, and have high customer satisfaction ratings. Our top-rated reverse osmosis system removes 85-92% of fluoride from drinking water. visit
CONCLUSION:
Groundwater contamination by and fluoride presents a significant global challenge in the quest for safe drinking water. While fluoride chemicals used in water fluoridation may contain contaminants, their concentrations are well below established safety limits. These pollutants remain dangerous even at low concentrations.
To avoid them you can periodically test your water to ensure that the filtration system or other measures you’ve implemented are effectively reducin and fluoride levels.
- You can check your water quality through the Life Water Report. You can also visit link and enter your zip code.
- Find out if your drinking water is contaminated with a FREE WATER REPORT of your area.
- By working together, we can create a healthy and safer environment for ourselves and future generations.
Visit Life Water Report and get a multi-stage filter system to improve your and your Family’s health.

