Cadmium, a naturally occurring element, can be found in various products and substances, posing health risks to individuals. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the presence of cadmium in drinking water, its sources, health effects, and measures to reduce exposure.
What is Cadmium?
Cadmium is a metallic element that occurs naturally in the Earth’s crust and soil. It has a wide range of industrial applications, including batteries, paints, pigments, coatings, and even inexpensive jewelry.
Cadmium Levels in the U.S. Population
In the Fourth National Report on Human Exposure to Environmental Chemicals (Fourth Report), CDC scientists measured cadmium in the blood of 8,372 participants aged one year and older and in the urine of 2543 participants aged six years and older who took part in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) during 2003–2004
Cadmium in Minnesota Waters
The presence of cadmium in water sources is a concern for public health. In Minnesota, cadmium concentration in groundwater varies, with only about 1 percent of samples from public drinking water supplies detecting levels greater than 0.1 parts per billion (ppb). Higher levels of cadmium in water can result from the use and disposal of cadmium-containing items, such as landfills.
The Minnesota Department of Health (MDH) has established a guidance value of 0.5 ppb for cadmium in drinking water.
Sources of Cadmium Exposure
Understanding how individuals are exposed to cadmium is crucial in preventative measures. Minnesotans may be exposed to cadmium through various sources, including:
1. Foods
Certain foods like leafy vegetables, sunflower seeds, peanuts, potatoes, organ meats, and shellfish contain cadmium.
Leafy plants, tobacco, and lettuce can absorb cadmium from the soil as they grow. Smoking tobacco products, including cigarettes, is a major source of cadmium exposure.
2. Drinking Water
Cadmium contamination of water sources can result from several factors, including natural erosion of cadmium-containing rocks, industrial waste, fertilizer contamination, pigment production, mine tailings, smelting, and corrosion of galvanized water pipes.
3. Jewelry and Pigments
Certain types of jewelry and pigments used in pottery finishes or cheap plastics can contain cadmium, posing a risk, especially for children who may mouth these objects.
4. Environmental Exposure: Cadmium exposure can occur through inhalation, environmental contamination, and ingestion. The most common environmental exposure is occupational exposure, especially in industries like electroplating, smelting, and mining, where workers may come into contact with cadmium fumes and dust.

Health Risks Associated with Cadmium
Cadmium exposure is associated with several health risks, including:
- Kidney Disorders: Cadmium has been linked to kidney disorders, which can have serious health implications.
- Bronchitis and Lung Damage: Cadmium inhalation can lead to bronchitis and lung damage.
- Anemia: Cadmium exposure is also associated with anemia, a condition characterized by a decrease in the number of red blood cells or a decrease in the amount of hemoglobin in the blood.
- Vulnerable Populations: Children are particularly vulnerable to cadmium exposure. Studies indicate that they are at risk of decreased bone strength, increased bone loss, and reduced birth weight. For pregnant mothers, cadmium exposure can affect breast milk, potentially impacting their infants.
- Nervous System Effects: Cadmium adversely affects the nervous system and results in learning and behavioral issues.
Cadmium Treatment Options
Are you concerned about drinking water quality? We’re here to help. Our website Life Water Report offers a quick and easy solution to ease your mind.
Get Informed | Check Your Water Quality
Start by accessing your Water Quality Analysis Report through our Free Life Water Report. This invaluable resource allows you to discover the levels of contaminants in your drinking water. It’s a simple and effective way to understand your water’s contamination level.
Short-Term Treatment
- Avoid Boiling Water: If you suspect cadmium contamination, avoid boiling your drinking water as it won’t remove cadmium. Boiling may even concentrate other contaminants.
- Avoid Smoking: Not smoking or being exposed to secondhand smoke can significantly reduce cadmium inhalation.
- Proper Product Handling: Properly handle products containing cadmium, such as “Ni-Cd” batteries, and ensure they are recycled appropriately.
- Point-of-Use Devices: Consider Point-of-use filters, such as water pitcher filters, which are equipped with special cartridges designed to reduce cadmium levels. They provide an easy and cost-effective solution for smaller water quantities. Click here for water Pitchers
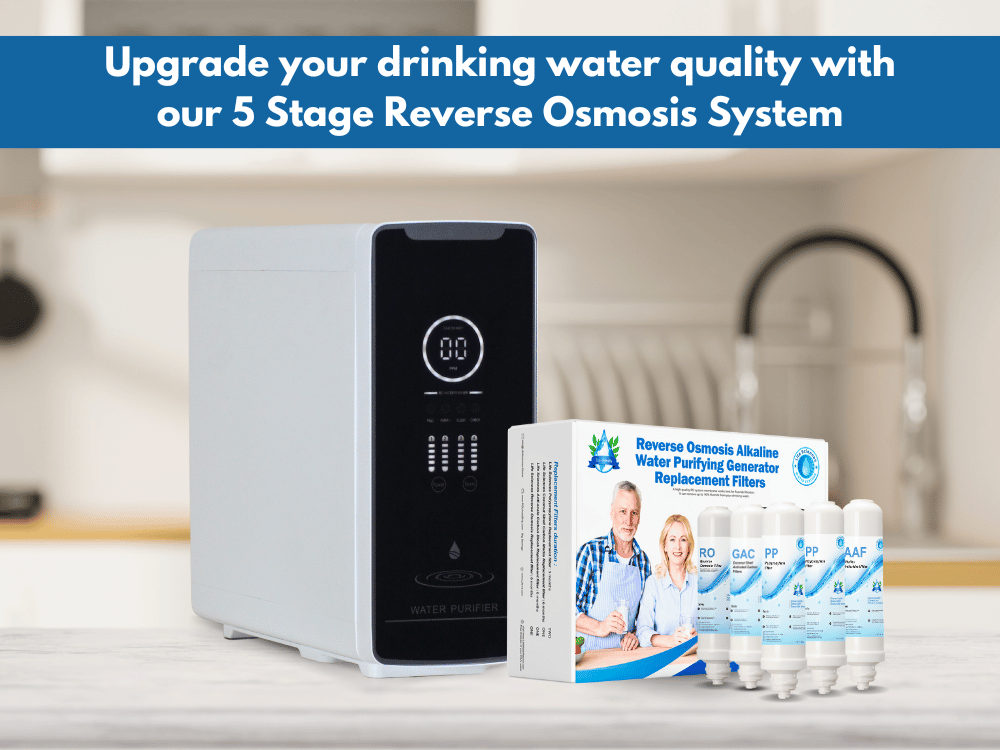
Long-Term Treatment
For long-term solutions, you need a water treatment system. Common technologies for cadmium removal include:
- Ion-Exchange Resin Filters: Ion-exchange filters replace cadmium ions with harmless ions, such as sodium or potassium. These systems remove cadmium and are often used in water softeners.
- Distillation Systems: Distillation involves boiling water and condensing steam to remove impurities, including cadmium. While effective, distillation can be energy-intensive and may not be the best choice for every household.
- Activated Carbon Filters: Some activated carbon filters remove heavy metals like cadmium from tap water. These filters adsorb contaminants onto the carbon surface.
- Reverse Osmosis (RO) Systems: RO systems are highly effective at removing cadmium and a wide range of contaminants from tap water. They use a semipermeable membrane to filter out impurities, ensuring clean and safe drinking water.
- Upgrade your drinking water quality with our 5 Stage Reverse Osmosis System, now available at a special price of $349.00. This advanced filtration solution eliminates up to 99% of dissolved contaminants, microbes, and heavy metals, providing you with safe and clean filtered drinking water. click here For More information
- Introducing our cutting-edge Life Sciences Reverse Osmosis Alkaline Water Purifying Generator – Tankless Technology, available at an unbeatable price of $597.00. This advanced system delivers clean and pure water and integrates innovative tankless technology, saving valuable space in your home.
- This system removes up to 98% of contaminants and enhances your water’s pH to a basic value of up to 8 or 9 pH.
- The specially formulated 5-stage filter removes chlorine, heavy metals, and a spectrum of contaminants. It adds essential minerals like calcium, magnesium, and potassium, along with antioxidants, providing water with a low negative ORP.
The Difference from 5-Stage Systems: While our 5-stage systems offer efficient filtration, our “Tankless Technology” system takes it a step further. It provides an increased filtration and purification capacity of 8 to 20 times, ensuring superior water quality. Click here for the Tankless RO water system
Conclusion
In conclusion, cadmium is an element found in various products and substances, including drinking water. It poses health risks, especially to children and older adults, and can harm the environment.
For the purest, healthiest, and most convenient drinking water solution, visit our website, Life Water Report, today.
Make the switch to a better lifestyle with our cutting-edge tankless water purification systems. Your journey to clean, alkaline, and antioxidant-rich water starts here.
- Minnesota Pollution Control Agency. 1999. http://www.pca.state.mn.us/ind ex.php/viewdocument.html?gid=
6312. - 2. Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR) 2012. http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/phs/p hs. asp?id=46&tid=15
- Bernard A. (2008). Cadmium & its adverse effects on human health. The Indian journal of medical research, 128(4), 557–564.
- Faroon O, Ashizawa A, Wright S, et al. Toxicological Profile for Cadmium. Atlanta (GA): Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (US); 2012 Sep. 3, HEALTH EFFECTS. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
books/NBK158834/
